This video features Jack Voorheis discussing the flaws in the current power production and delivery systems and advocating for solar energy as a solution. He highlights issues with traditional power sources like coal and nuclear power, emphasizing their inefficiency and environmental impact. “The Current Power System is Flawed and Unsustainable”.
Jack argues that solar power, being generated where it’s used, mitigates transmission losses and dependence on utility companies. He stresses the increasing demand for electricity due to electrification trends and cloud computing. Jack predicts a significant rise in electrical costs and urges viewers to consider solar as a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative. He concludes by mentioning the varying attractiveness of solar incentives across different states.
The methods we use to generate and distribute power are riddled with inefficiencies and flaws. From the way we produce electricity to the methods of transporting it across vast distances, the current systems are unsustainable and burdened with inefficiencies. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the shortcomings of our existing power production and distribution methods and explore the need for a paradigm shift towards more efficient and sustainable alternatives.
Inefficiencies in Power Production makes the current power system flawed and unsustainable.
- Reliance on Non-Renewable Resources: The predominant reliance on non-renewable resources such as coal, natural gas, and nuclear energy for power production is a major inefficiency. These resources are finite and environmentally damaging to extract. Additionally, the process of burning fossil fuels to produce electricity is inherently inefficient, with significant energy loss in the form of heat during combustion.
- Centralized Power Plants: The centralized nature of power plants contributes to inefficiencies in power production. Large-scale power plants are often located far from population centers, necessitating long-distance transmission of electricity. This results in energy loss during transmission, as electricity encounters resistance and dissipates as heat along power lines.
- Lack of Flexibility: Traditional power plants, particularly those reliant on fossil fuels and nuclear energy, lack flexibility in responding to fluctuations in demand. These plants operate on fixed schedules and are slow to ramp up or down in response to changes in demand, resulting in inefficiencies during periods of low demand or sudden spikes in consumption.
Inefficiencies in Power Distribution:
- Aging Infrastructure: The infrastructure used to distribute electricity, including power lines, substations, and transformers, is aging and prone to inefficiencies. Much of this infrastructure was built decades ago and is in need of modernization and upgrades to improve efficiency and reliability.
- Energy Loss during Transmission: The transmission of electricity over long distances results in energy loss due to resistance in power lines. This loss, known as line loss, occurs as electricity encounters resistance from the conductive materials used in power lines, leading to heat dissipation and reduced efficiency.
- Lack of Grid Resilience: The centralized nature of power distribution grids makes them vulnerable to disruptions from extreme weather events, cyber-attacks, and other threats. When a section of the grid fails, it can lead to widespread power outages and economic disruptions, highlighting the need for more resilient and decentralized grid architectures.
The Path to Efficiency and Sustainability:
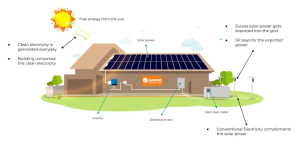
- Transition to Renewable Energy: One of the most effective ways to improve the efficiency and sustainability of power production is to transition to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Unlike fossil fuels and nuclear energy, renewable energy sources produce electricity with minimal environmental impact and can be harnessed close to where it is needed, reducing transmission losses.
- Decentralized Power Generation: Embracing decentralized power generation through distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar panels, microgrids, and community solar projects can improve efficiency and resilience in power distribution. By generating electricity closer to where it is consumed, decentralized systems reduce the need for long-distance transmission and minimize energy loss.
- Smart Grid Technologies: Investing in smart grid technologies such as advanced metering infrastructure, grid automation, and energy storage can improve the efficiency, reliability, and resilience of power distribution systems. These technologies enable better monitoring and management of electricity flows, optimize grid operations, and facilitate integration of renewable energy sources.
Conclusion: The Current Power System is Flawed and Unsustainable. The inefficiencies inherent in current power production and distribution systems are unsustainable and pose significant challenges to our energy future. By transitioning to renewable energy, embracing decentralized power generation, and investing in smart grid technologies, we can improve efficiency, resilience, and sustainability in our energy systems. It’s time to rethink how we produce and distribute power and embrace more efficient and sustainable alternatives for a brighter energy future.
Inefficiencies in Power Production:
- Reliance on Non-Renewable Resources:
- Drawdown.org: https://drawdown.org/ (Explore solutions for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.)
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA): https://www.irena.org/ (Provides data and analysis on renewable energy potential.)
- Centralized Power Plants:
- The Institute for Local Self-Reliance: https://ilsr.org/ (Promotes community-based energy solutions.)
- Microgrid Knowledge: https://www.microgridknowledge.com/ (Provides resources and information on microgrids.)
- Lack of Flexibility:
- Smart Grid Coalition: http://www.drsgcoalition.org/ (Advocates for smart grid technologies.)
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): https://www.nrel.gov/ (Conducts research on renewable energy and grid integration.)
Inefficiencies in Power Distribution:
- Aging Infrastructure:
- American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): https://infrastructurereportcard.org/ (Issues annual infrastructure report cards.)
- The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act: https://www.whitehouse.gov/build/ (Federal legislation to upgrade infrastructure.)
- Energy Loss during Transmission:
- Grid Alternatives: https://gridalternatives.org/ (Promotes community-based renewable energy.)
- National Grid: https://www.nationalgrid.com/ (UK electricity transmission system operator.)
- Lack of Grid Resilience:
- Resilient Energy Collaborative: https://www.resilience.org/energy/ (Promotes resilient energy systems.)
- Federal Energy Management Agency (FEMA): https://www.fema.gov/ (Provides resources for disaster preparedness and response.)
The Path to Efficiency and Sustainability:
- Transition to Renewable Energy:
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): https://www.seia.org/ (Advocates for the solar energy industry.)
- American Wind Energy Association (AWEA): https://cleanpower.org/news/awea-wind-energy-now-top-source-of-renewable-electricity/ (Advocates for the wind energy industry.)
- Decentralized Power Generation:
- The Energy Democracy Initiative: https://energydemocracy.us/ (Promotes community ownership of renewable energy.)
- Community Power Network: https://www.communitypowermn.org/ (Supports community solar projects.)
- Smart Grid Technologies:
- GridWise Alliance: https://gridwise.org/ (Promotes smart grid technologies.)
- The Edison Electric Institute (EEI): https://www.eei.org/ (Electric utility industry association.)
Additional Resources:
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 7: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal7 (Affordable and clean energy.)
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): https://www.ipcc.ch/ (Provides scientific assessments on climate change.)